While creating portfolios for clients, the most important decision to be made by the financial advsior is the allocation of clients' funds among asset classes. The two major asset classes are equities and fixed income securities. Other asset classes like real estate, private equity, art, commodities, and hedge funds are referred to as “alternative asset classes.”
While equities have the potential to create significant wealth for investors over the long term, debt or fixed income securities have an important role to play in the portfolios of individual and corporate investors.
What is Debt
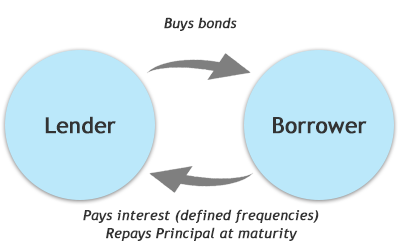
In layman terms, debt is an “IOU” issued by the borrower to the person who is lending money. It is a financial obligation of an entity (individual, corporate, government or government - backed body) that promises to pay a pre-determined sum of money at pre-determined future dates. The entity that promises to make the payment is called the issuer of the security. Some examples of issuers are central governments like the Government of India, government related agencies like the Reserve Bank of India, government backed companies like NHAI, REC, HUDCO etc., state governments like Gujarat, Rajasthan, Tamil Nadu etc., and corporates including banks like Tata Group, HDFC, DHFL, Bank of India, IDBI Bank, Vijaya Bank etc.
While fixed income securities, bonds and debt are used interchangeably, there are two general categories of fixed income securities:
- Debt obligations
- Preferred Stock
In case of debt, there are two parties involved: borrower or issuer of the security and lender or creditor. The issuer agrees to pay a fixed rate of interest on the principal amount borrowed to the lender or creditor.
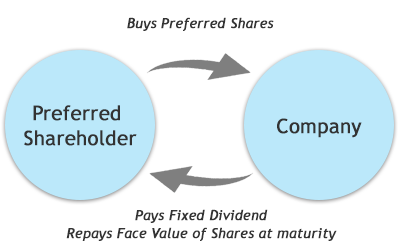
Preferred stock represents ownership interest in a company. The preferred stock holders receives dividend payments which represents a distribution of the company's profits. Unlike common or ordinary shareholders, preferred shareholders receive a contractually fixed dividend which has priority over the dividends paid to common shareholders. In case the company were to wind up its operations, preferred shareholders are given preference over the ordinary shareholders. Therefore, preferrred stock is a form of equity that has bond like characteristics.